According to the international standard ISO/TR 25901-3, "welding with pressure (2.1.2) whereby the workpieces are kept in contact under specified continual pressure and are heated either on their faying surfaces, or in their entirety at a defined temperature over a controlled time. This results in local plastic deformation and thereby intimate contact of the surfaces and diffusion of the atoms through the interface. This produces complete continuity of the material. The operation can take place in a vacuum, under a gas shield or in a fluid, preferably without the addition of a filler metal."
Diffusion bonding is also known as diffusion welding or diffusion joining.
In layman’s terms, Plates can be directly joined by just heating and pressing them together.
Also it is possible to manufacture products with complex internal channels by stacking many etched thin sheets.
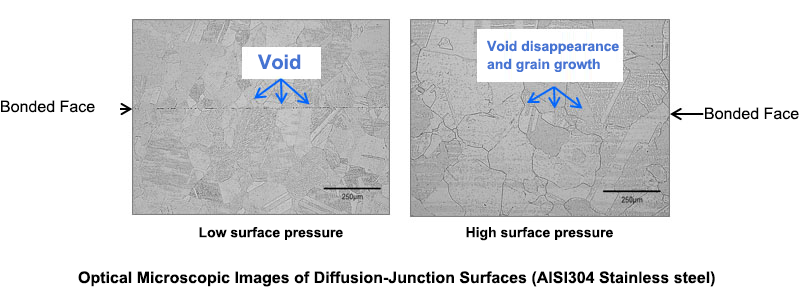
①High bond strength
・Bonded by atomic-level diffusion
・It is possible to join on a face rather than on a point or line like a weld.
・The bonding strength is almost as good as the base material.
②Cleanliness Bonding Process
・Direct bonding is possible.
・No brazing materials or adhesives other than the base material are used.
③Small amount of deformation
・Bonding is possible without melting the base metal because it is possible to bond below its melting point.
・It is possible to join micro-fabricated products such as photo-etched products.
④Bonding dissimilar materials is available
・A variety of materials as well as similar materials can be joined because they are bonded by atomic diffusion.
・There have been a number of reports in recent years on the joining of various combinations of materials.
Ex.Fe+Cu, Cu+Al, Fe+Fe, Al+Ceramics, Cu+Ceramics, etc.
| Heat Sinks, Water Cooling Plates | Heat Exchangers | Dissimilar Bonding |
 | 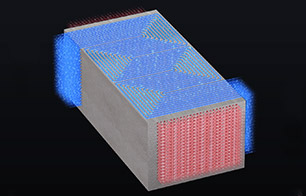 | 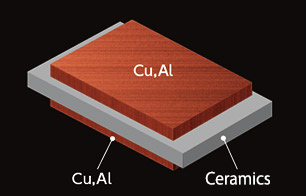 |
Heat dissipation components such as heat sinks and vapor chambers for mobile devices, automotive electronics, etc. are produced by diffusion bonding. | Metal flat plate with etched groove to be stacked, and bonded by diffusion phenomenon of metal. The heat exchangers are known as Micro Channel Heat Exchangers (MCHE) or Printed Circuit Heat Exchangers (PCHE). | Metals such as copper and aluminum are directly bonded to the ceramic substrate. Brazing material or insert material may be inserted into the joint surface to improve the joining performance. |