Aug. 28, 24
Sintering is the process of heating a powder to a certain temperature and holding it for a certain time, then cooling the material to obtain a product with the desired properties. The entire process of special heat treatment is called sintering.
Sintering turns a porous powder briquette into a product with certain textures and properties. Although the properties of the product are related to many factors prior to sintering, in many cases the sintering process has a significant or even dominant effect on the organization and properties of the final product.
According to the principles of powder metallurgy classification of sintering, cemented carbide sintering is a multiphase liquid phase sintering. From the process characteristics of the sintering process, the sintering of cemented carbide can be done by hydrogen protection, vacuum sintering, hot press sintering, hot isostatic pressing, etc.
On Sale 10MPa Gas Pressure Sintering Furnace
The most readily observable changes in the sintered carbide billet are the shrinkage of the billet volume, the increase in strength, and the metallic luster of the alloy surface. Typically, the porosity of the pressed billet is about 50%, while the product should normally be less than 0.2%, which is almost completely dense. The briquettes should also be held lightly before sintering to avoid damage during the production process. The sintered product has the strength to withstand a variety of working conditions.
Unlike the powder forming process, the change in the nature of the sintered material indicates a qualitative change between the powder particles during the sintering process, i.e. the bond between the alloy particles replaces the contact between the powder particles, making the alloy form a solid whole, resulting in excellent physical and mechanical properties.
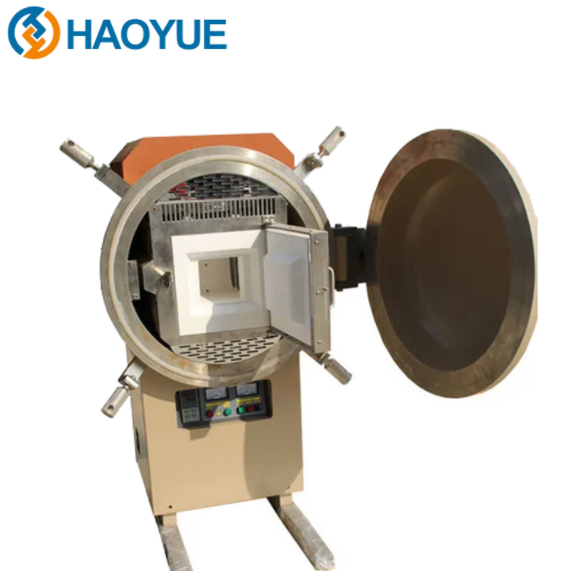

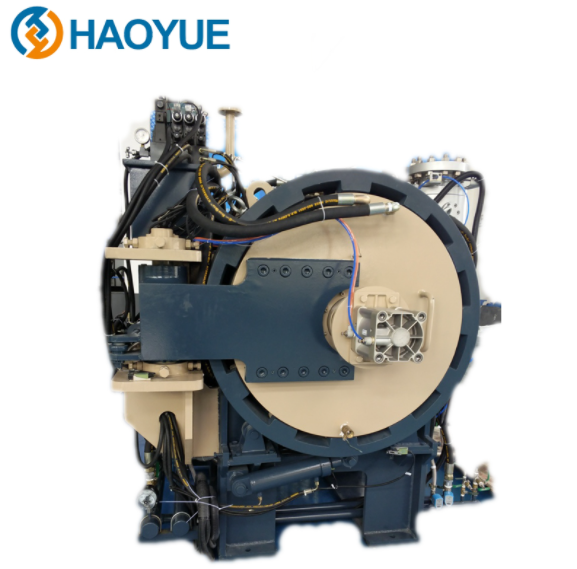
High Quality A1-17 Hydrogen Sintering Furnace
Cemented carbide sintering process can be divided into four basic stages.
In the first stage, the sintering hoop changes as follows.
1) Removal of the forming agent. At the beginning of sintering, as the temperature increases, the forming agent gradually cracks (e.g., rubber) or vaporizes (e.g., paraffin) and excludes the sintered body. At the same time, the molding agent is more or less carbonized by the sintered body.
2) Redox on the powder surface. When sintering in hydrogen, hydrogen can reduce cobalt and tungsten oxides. When sintering in vacuum, the reduction of carbon at that temperature is not strong.
3) The state of powder particles change each other. At this temperature, the contact stress between the powder particles is gradually eliminated, the combined metal powder starts to recover and recrystallize, the particles start to diffuse on the surface, and the strength of the pressed billet increases.
Eutectic temperature is the temperature at which the eutectic liquid phase starts to appear in the sintered body when the temperature is gradually increased. For WC-Co, the eutectic temperature at equilibrium sintering is 1340%.
At the temperature before the appearance of the liquid phase, in addition to the process continued in the previous stage, some solid phase reactions in the sintered body intensify, the diffusion rate is accelerated, and the plastic flow of the particles is enhanced, so that the sintered body shows a significant shrinkage.
When the liquid phase appears in the sintered body, the shrinkage of the sintered body is quickly completed, and the carbide grains grow and form a skeleton, thus laying down the basic organization of the alloy.
In this stage, the microstructure of the alloy and the composition of the bonded phase change depending on the cooling conditions. After cooling, the final microstructure of the alloy is obtained.
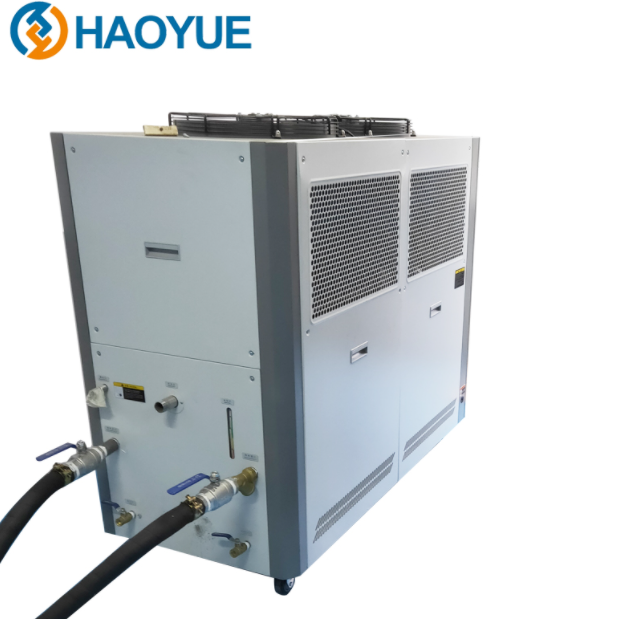

HAOYUE sintering furnace has the distinctive characteristics of fast heating rate, short sintering time, controllable structure, energy saving and environmental protection. It can be used to prepare metal materials, ceramic materials, composite materials, nano block materials, amorphous block materials, gradient materials. If you wanna know more info, please feel free to contact us.