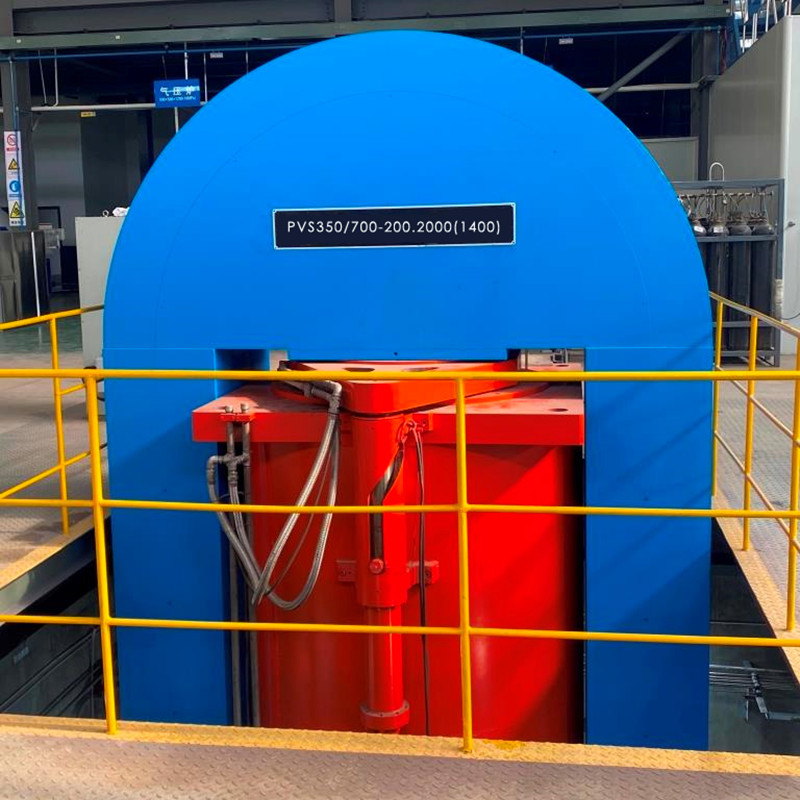
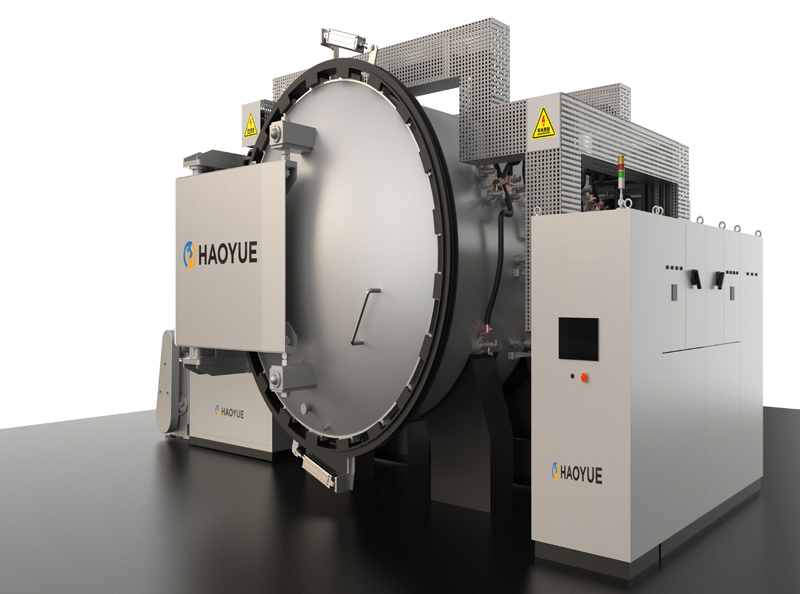
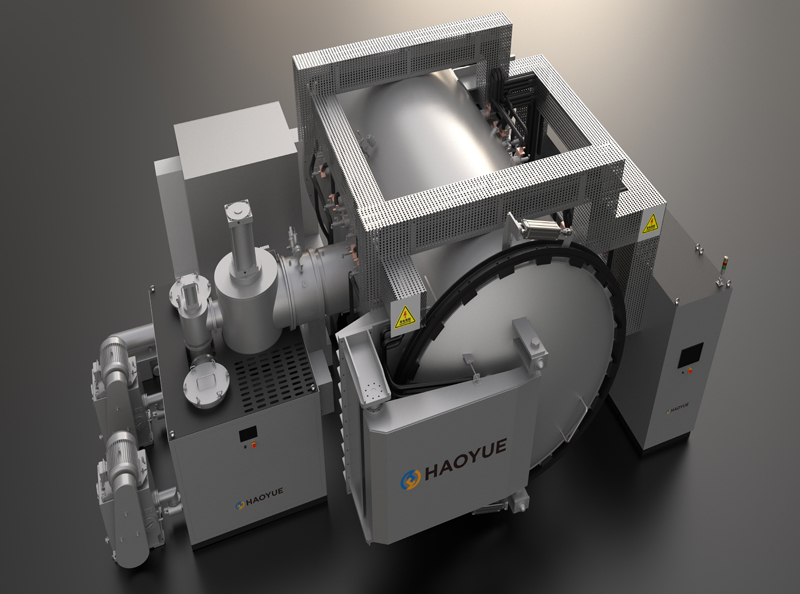
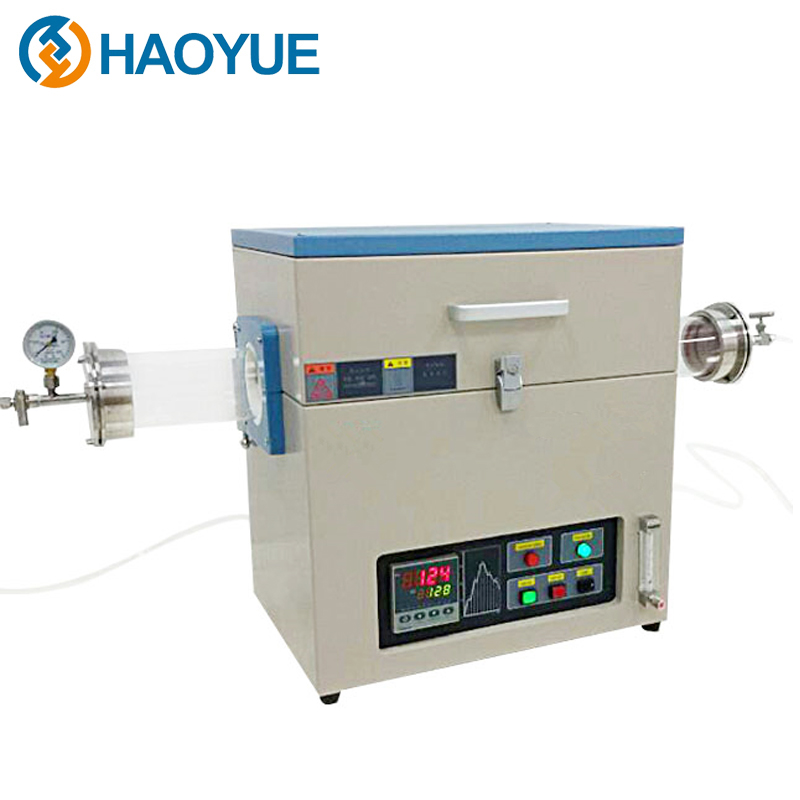
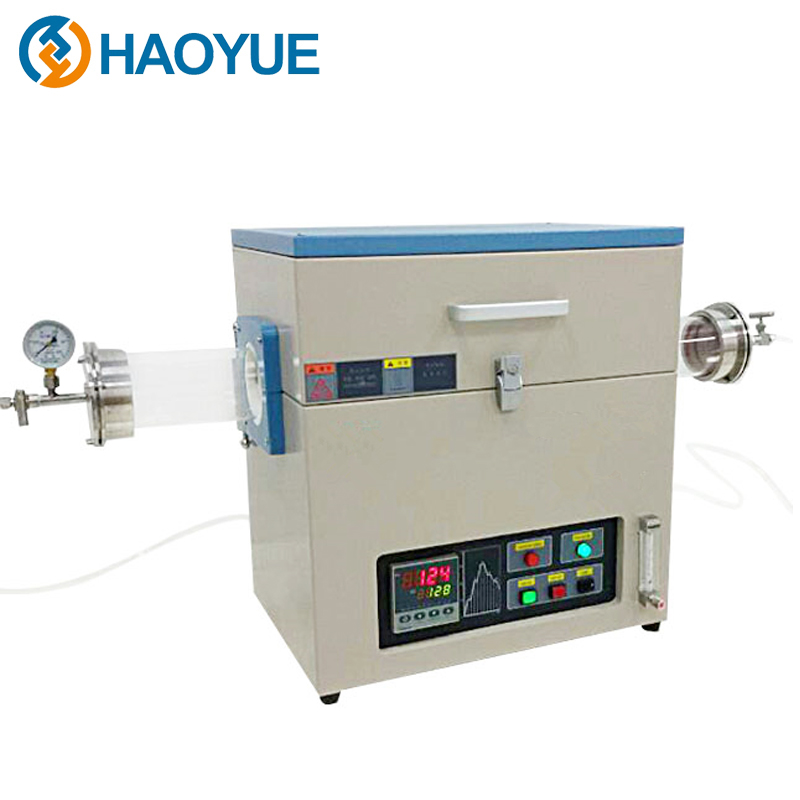
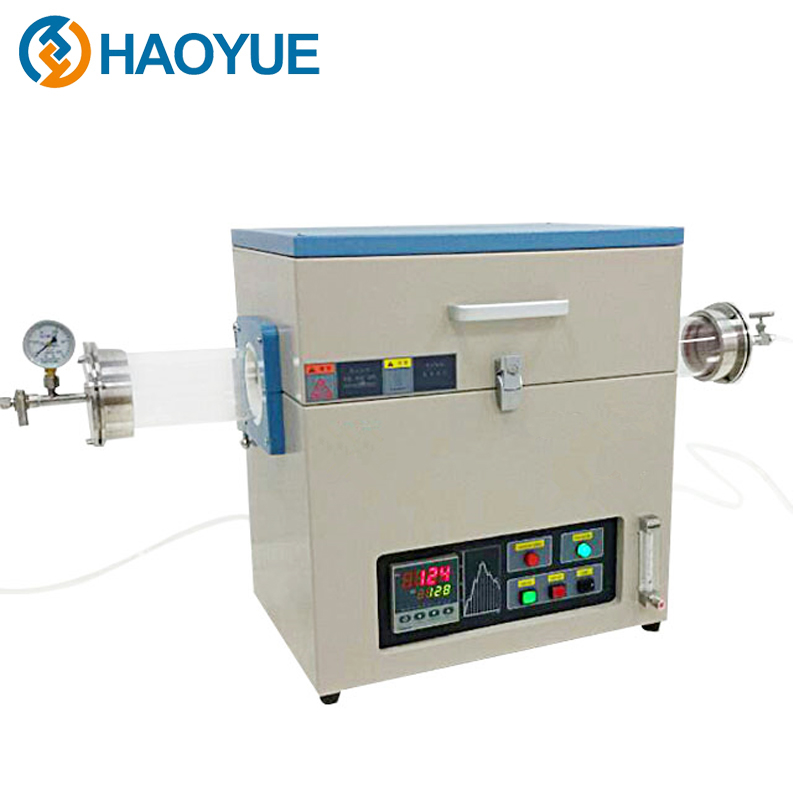
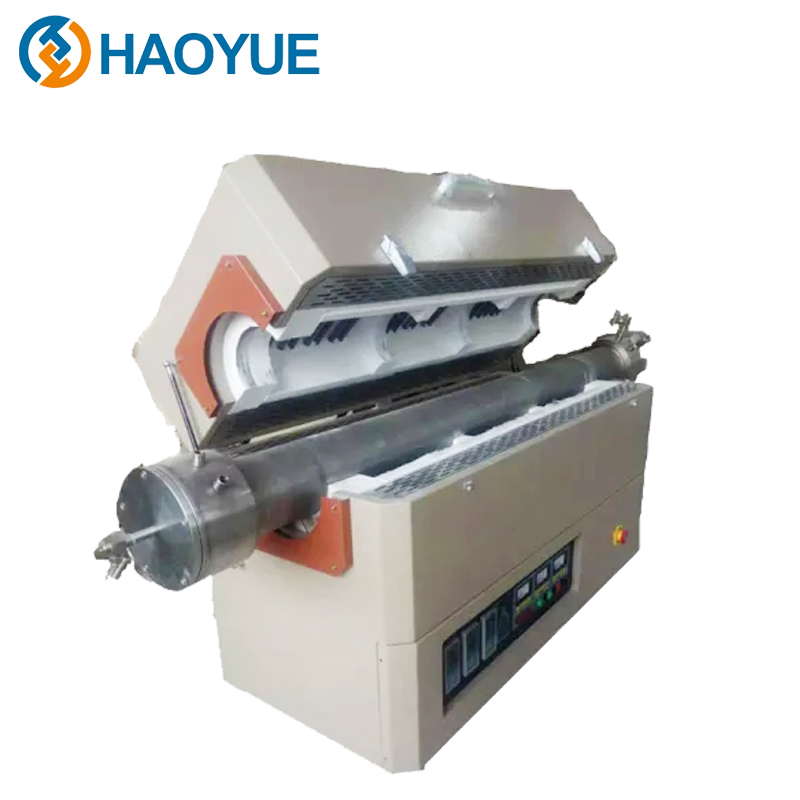
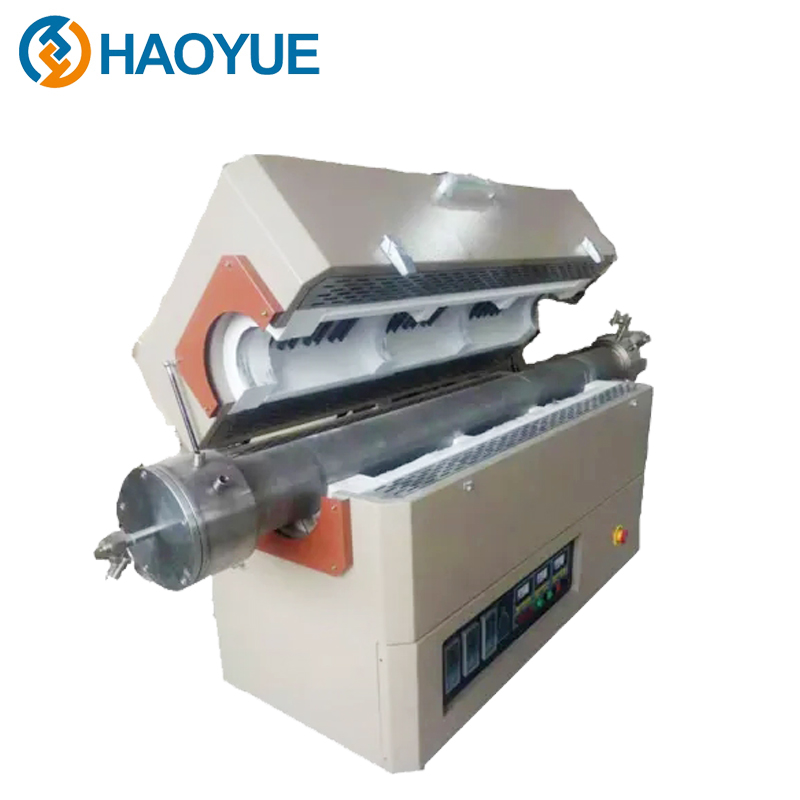
2000℃ Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) Furnace
The working principle of the hot isostatic press is a process in which the temperature and pressure are uniformly applied to the treated parts in the sealed ultra-high pressure vessel according to Pascal principle, so that their performance is obviously better than that of other methods. The pressure medium is usually argon and nitrogen. Reasonable temperature and pressure can better control the growth of grains and the identity of structure and performance, so that the performance of parts treated by hot static press is superior.
Technical Data
1.Working pressure: 200MPa;
2. hot zone diameter: Φ 300mm;
3.hot zone height: h600mm;
4. Maximum working temperature of C / C heating furnace: 2000 ℃, common working temperature: 1700 ℃;
5. Maximum working temperature of molybdenum lanthanum alloy heating furnace: 1400 ℃, common working temperature: 1300 ℃;
6.Temperature measuring thermocouple of C / C heating furnace: wre3 / 25 (JB / t12529-2015). When the working temperature is ≥ 1700 ℃, the service life of the thermocouple is once;
7.Temperature measuring thermocouple of molybdenum lanthanum heating furnace: s grade I (GB / t1598-2010);
8.Working medium: high purity argon (99.99%);
9. Vacuum degree (room temperature, no workpiece): ≤ 100Pa;
10.Vacuum pumping time (room temperature, no workpiece): t ≤ 15min;
11.Temperature rise time of C / C heating furnace (without workpiece): room temperature ~ 1700 ℃ ≤ 3H;
12. Heating time of molybdenum lanthanum alloy heating furnace (without workpiece): room temperature ~ 1300 ℃ ≤ 3H;
13.0 ~ 70MPa pre pressurization time (without workpiece): ≤ 2H (pressurize to the pre pressurization pressure, and the pressure will naturally expand to 200MPa after the temperature rises to 2000 ℃;
14. Loading method: top loading;
15. Power supply of the whole machine: TN-S incoming line, AC380V, 50Hz; Or local national power supply standards
16. Installation method: ground installation.
Specifications
| Type | Temperature | pressure | Uniform temperature | vacuum degree | Gas | Power supply | Heating time | Machine weight | Installation area | Heater material | Loading mode |
| ℃ | MPa | ℃ | (Pa);option | option | KW | Hour | Ton | ㎡ | |||
| PVSgr-12/25-2000.200 | 2000 | 200 | ≤±10 | 100 | Ar or N2 | 80 | ≤4 | 110 | 32.5 | Gr/Mo | TL |
| PVSgr-15/30-2000.200 | 2000 | 200 | ≤±10 | 100 | Ar or N2 | 115 | ≤4 | 127 | 36.5 | Gr/Mo | TL |
| PVSgr-26/35-2000.200 | 2000 | 200 | ≤±10 | 100 | Ar or N2 | 310 | ≤3 | 72 | 36.5 | Gr/Mo | TL |
| PVSgr-30/50-2000.200 | 2000 | 200 | ≤±10 | 100 | Ar or N2 | 450 | ≤4 | 100 | 252 | Gr/Mo | TL |
Application
In the spacecraft manufacturing industry, hot isostatic pressing is mainly used to manufacture dense carbon structural parts, such as the rudder of rocket and the nozzle throat lining of solid rocket motor.
Precision castings of various alloys, such as superalloy turbine blades, cast titanium gearbox and aluminum alloy castings of turbocharger, can eliminate internal porosity and shrinkage after hot isostatic pressing densification, and improve performance, reliability and service life. Hot isostatic pressing is also an effective method to repair core parts to prolong service life.
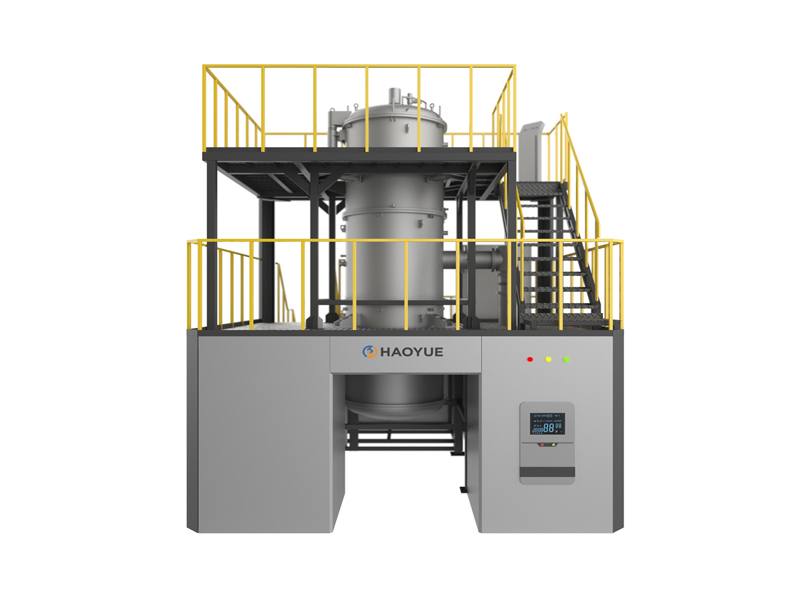
Main Ingredients
| Main components | |
| isostatic pressure device | 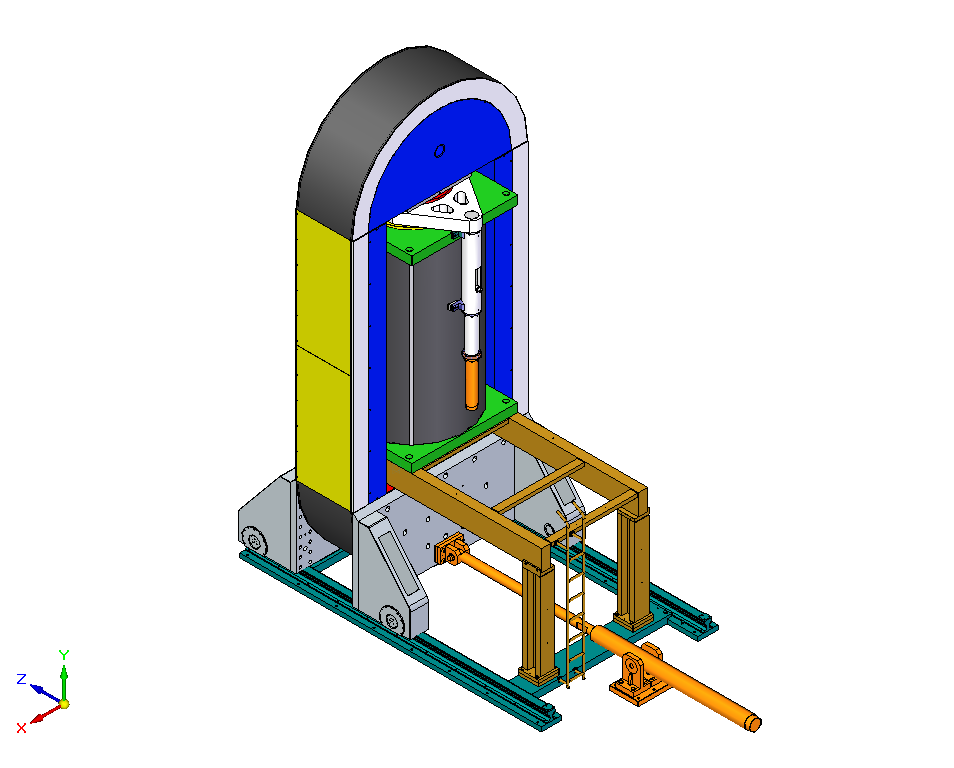 |
| gas system | 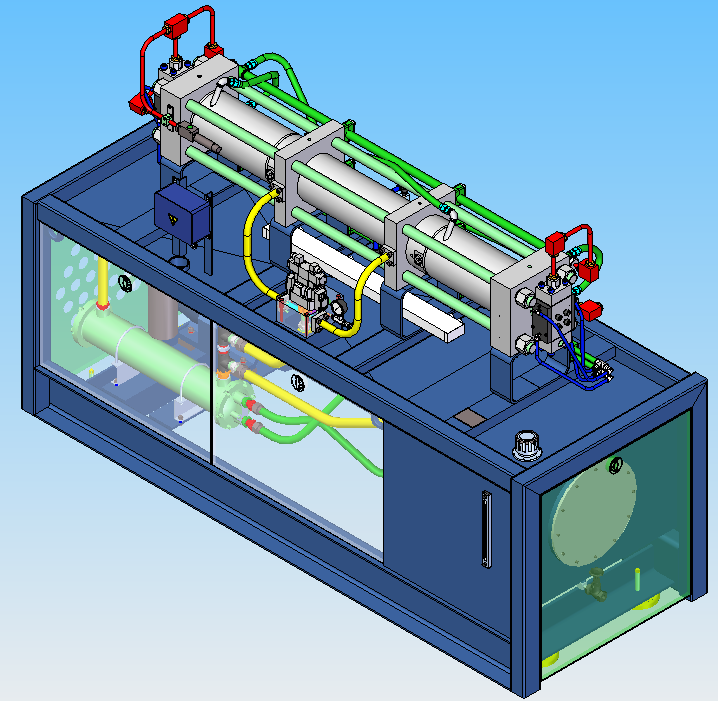 |
| cooling system |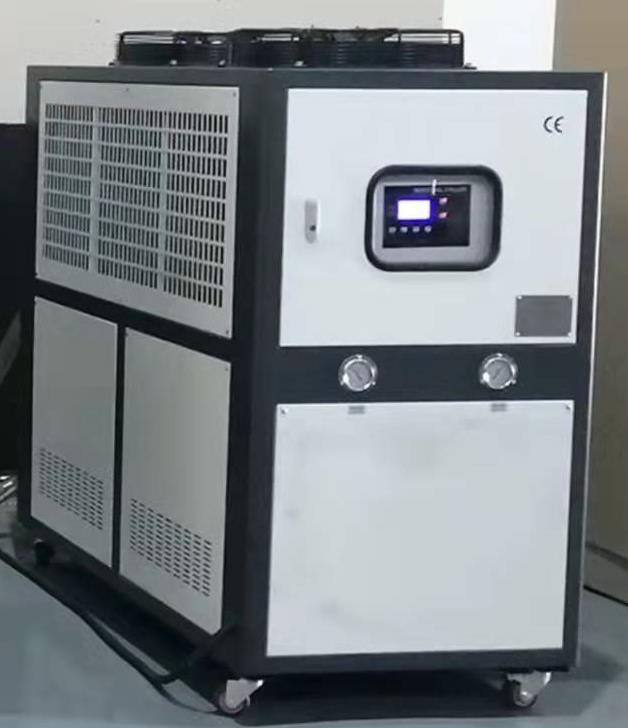  |
| electrical system |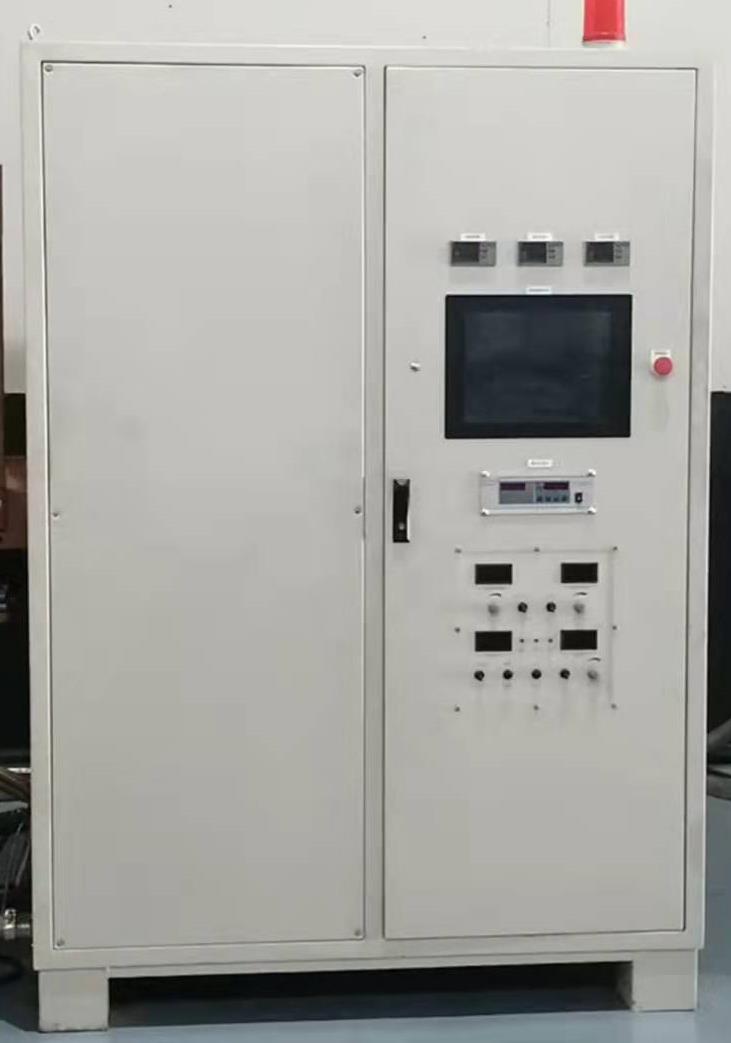  |
Tags






















