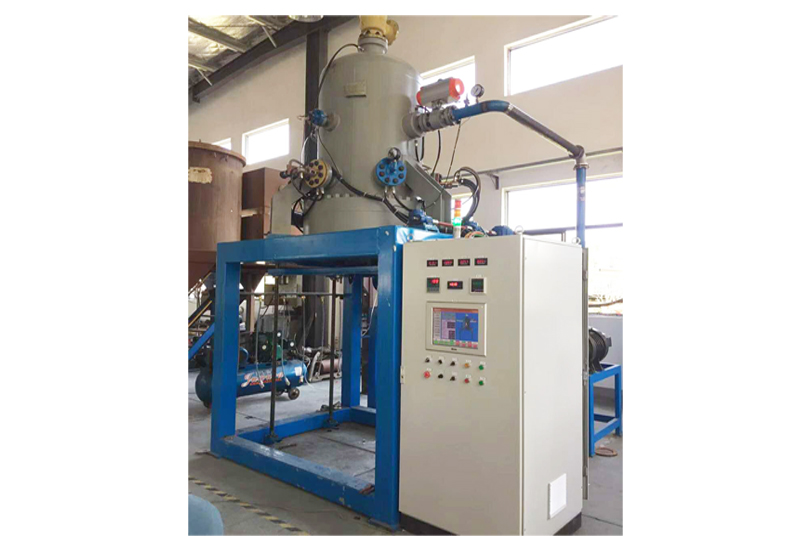
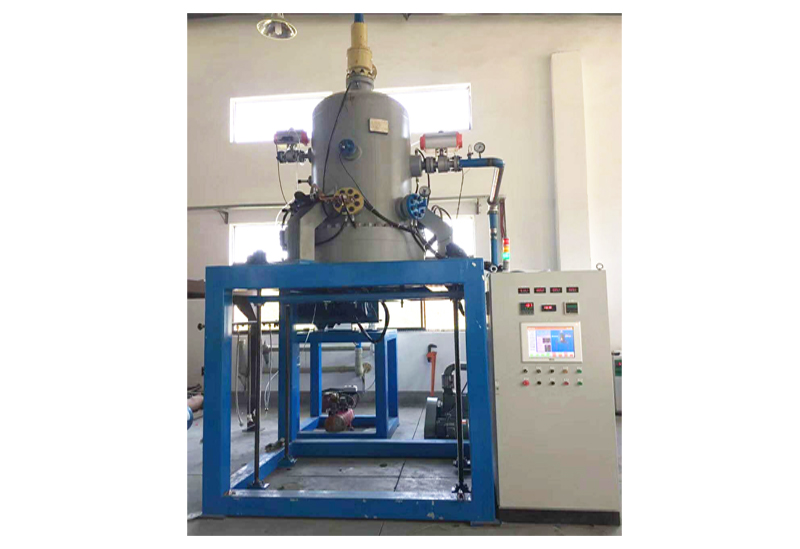
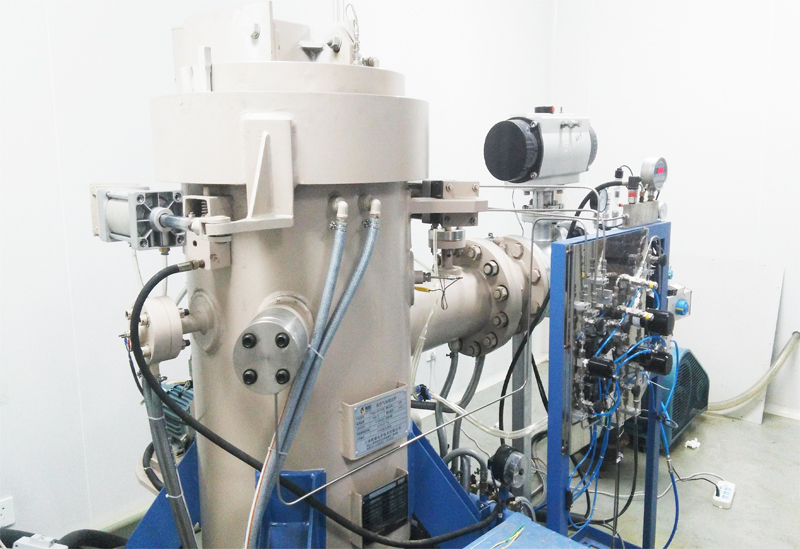
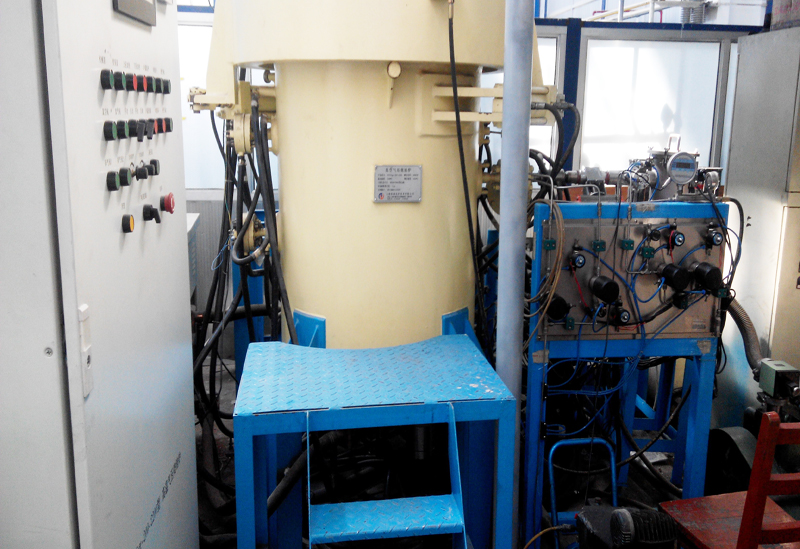
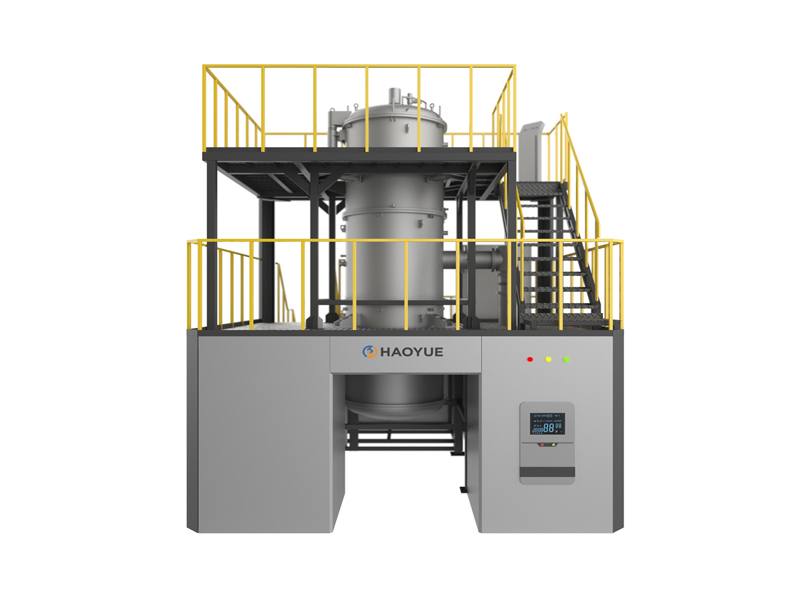
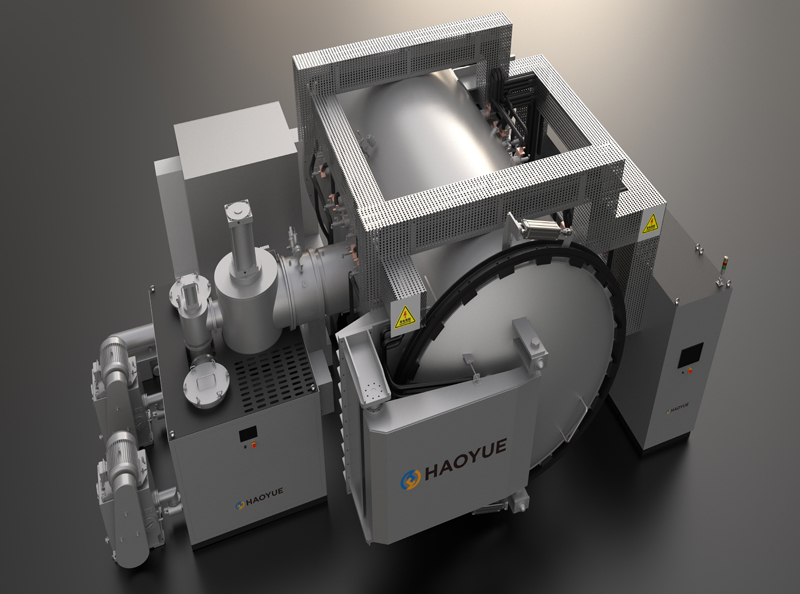
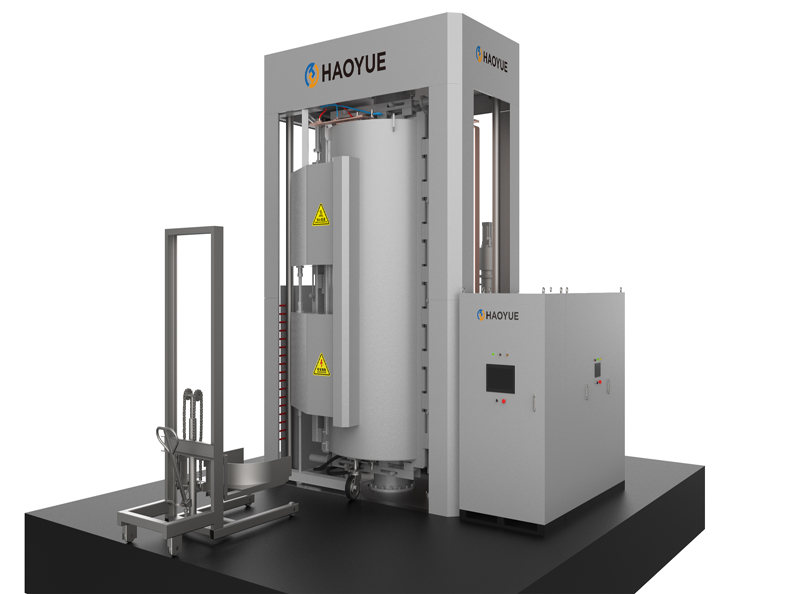
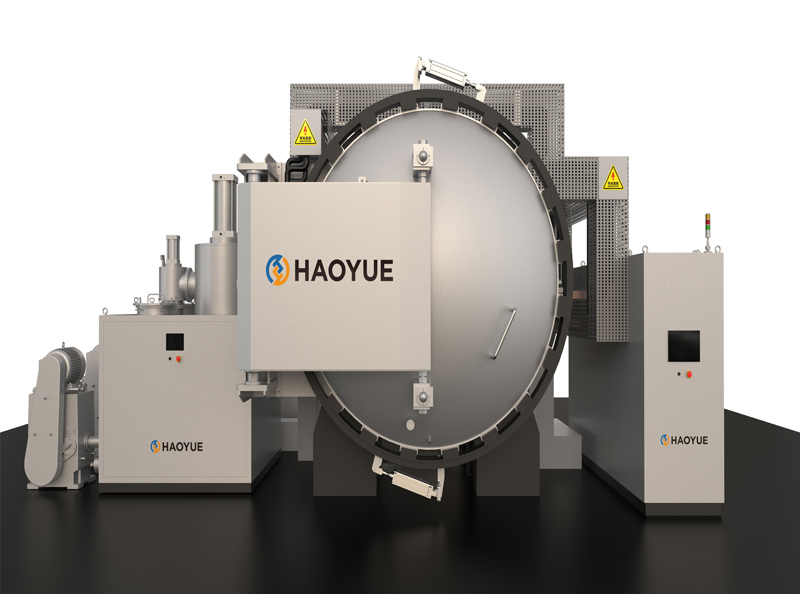
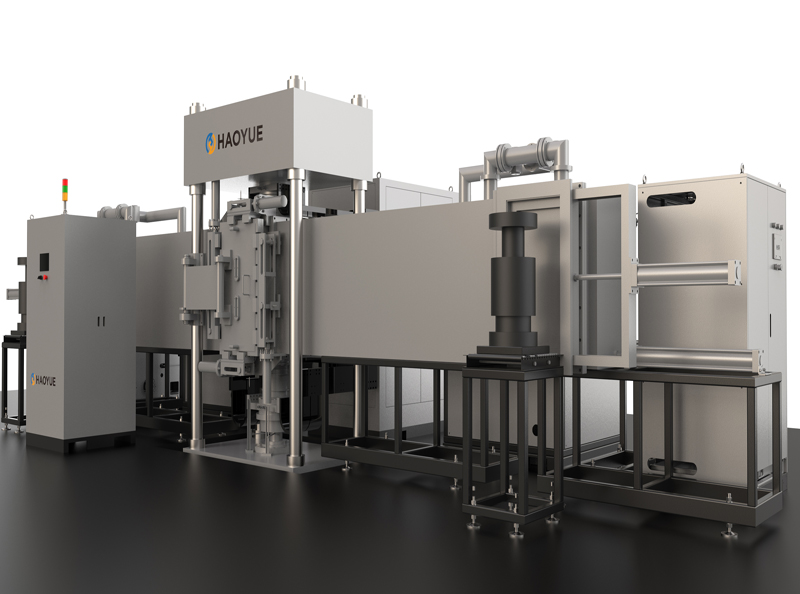
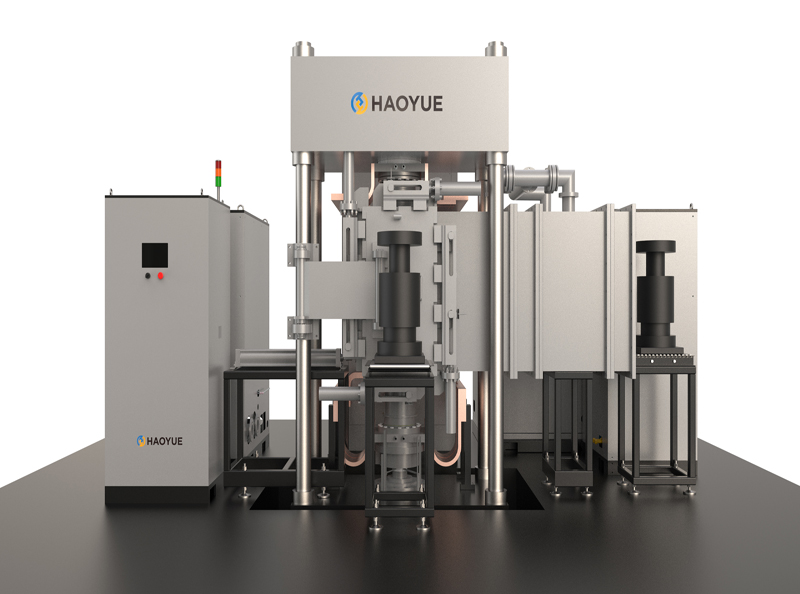
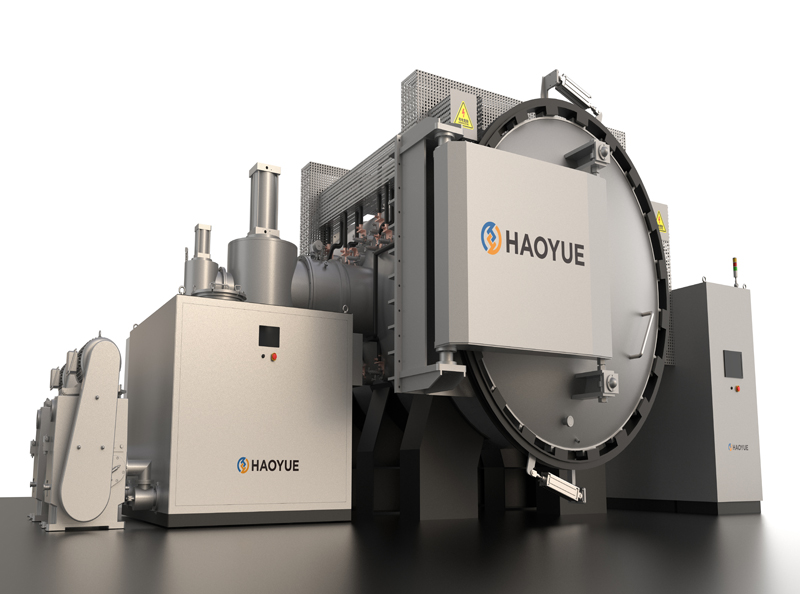
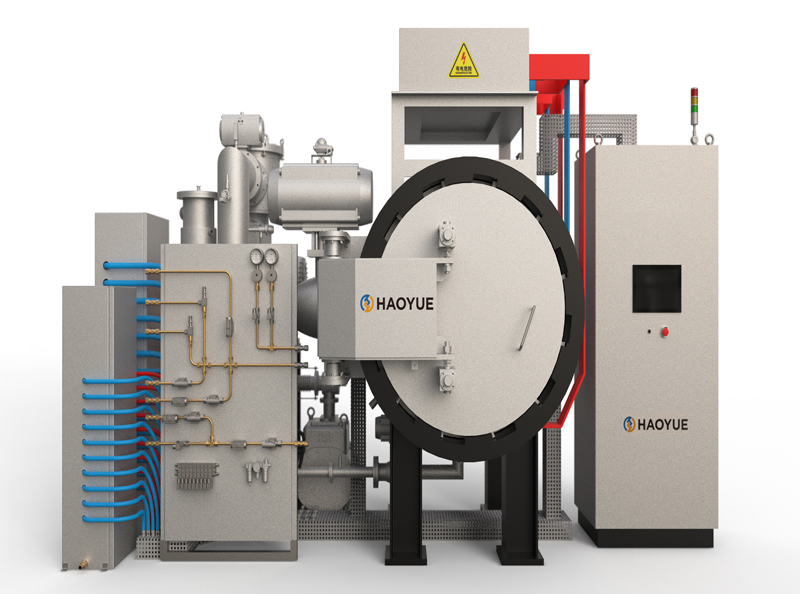
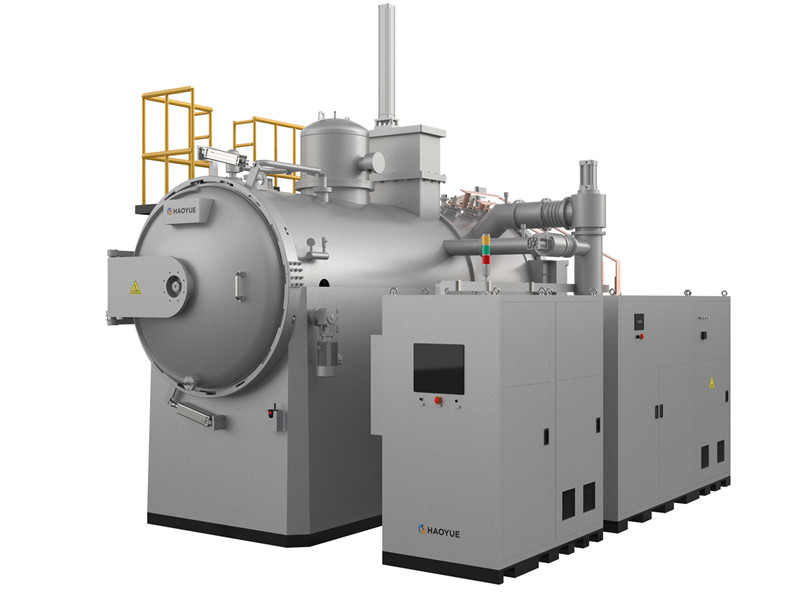
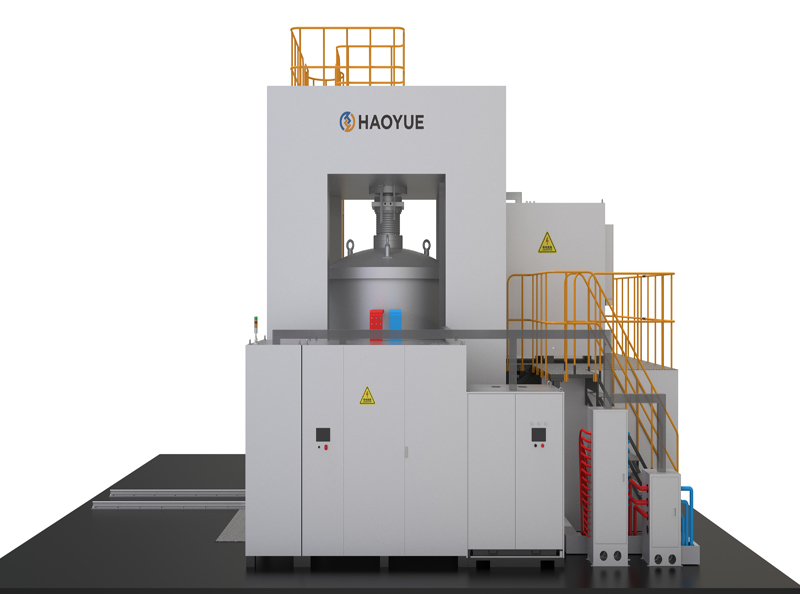
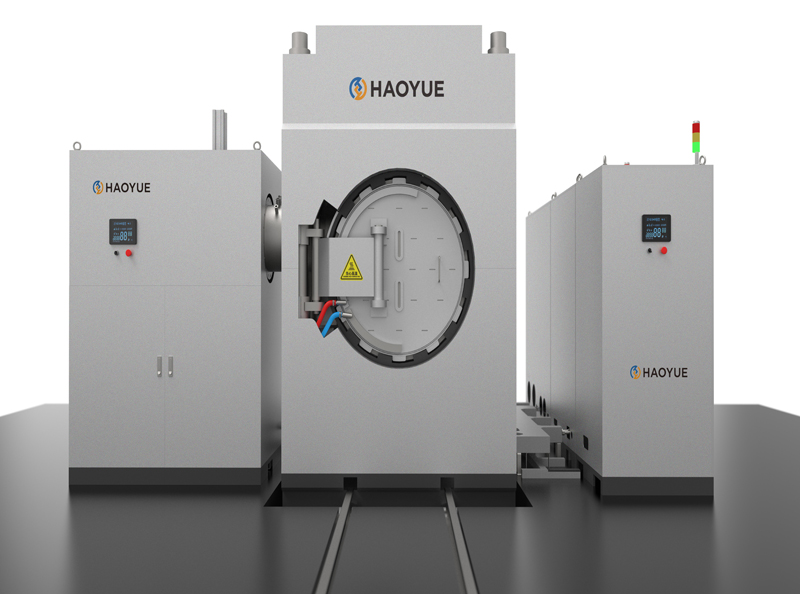
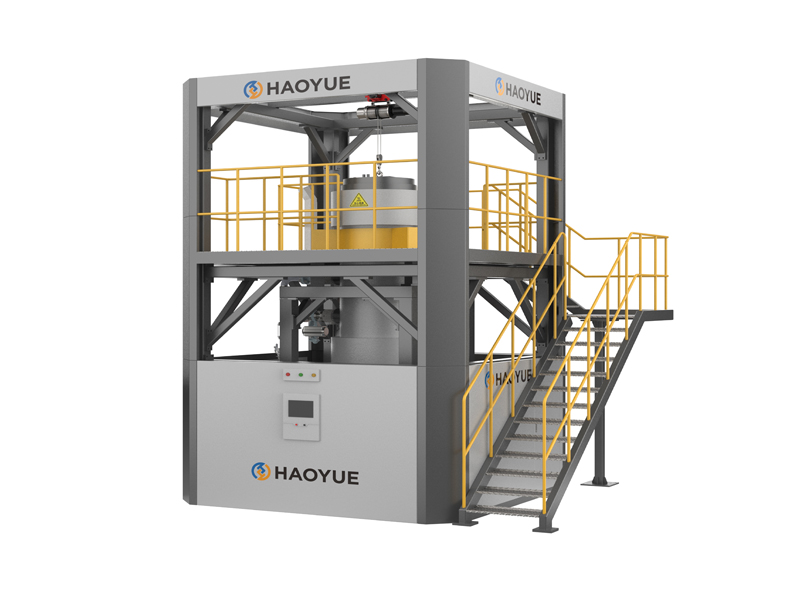
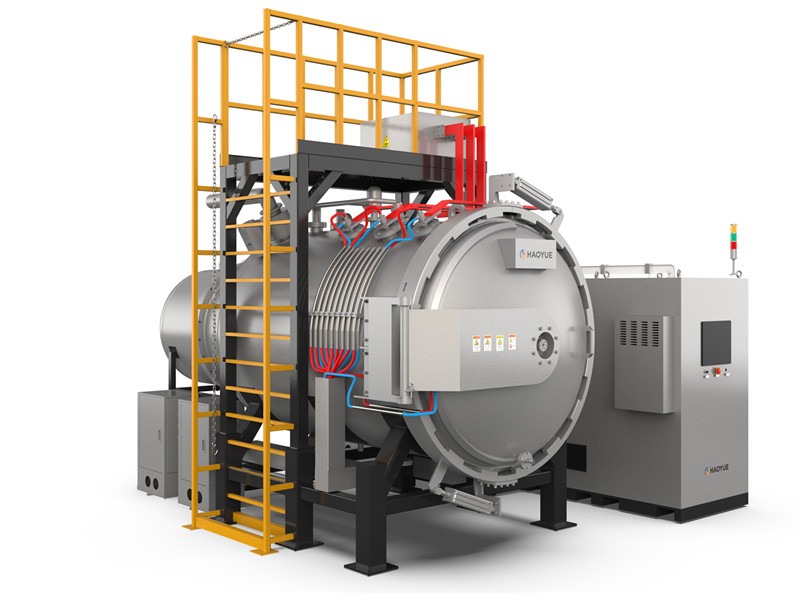
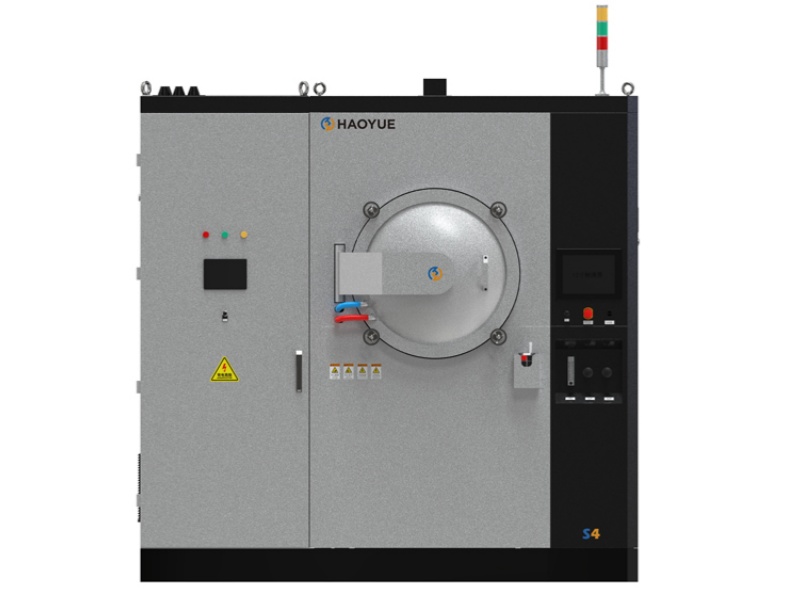
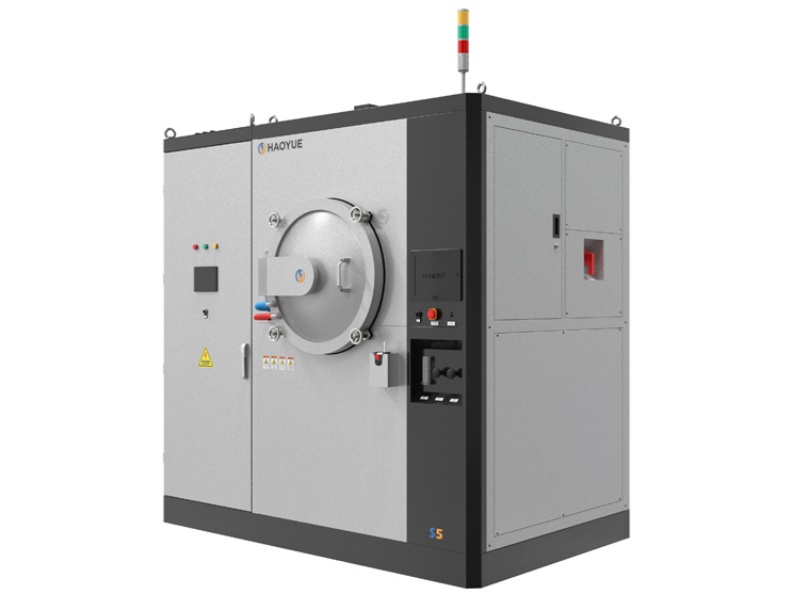
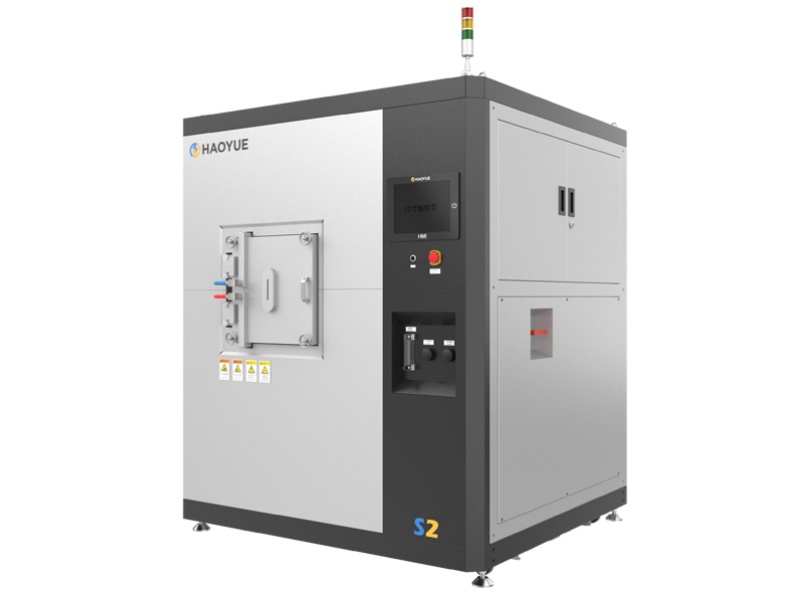
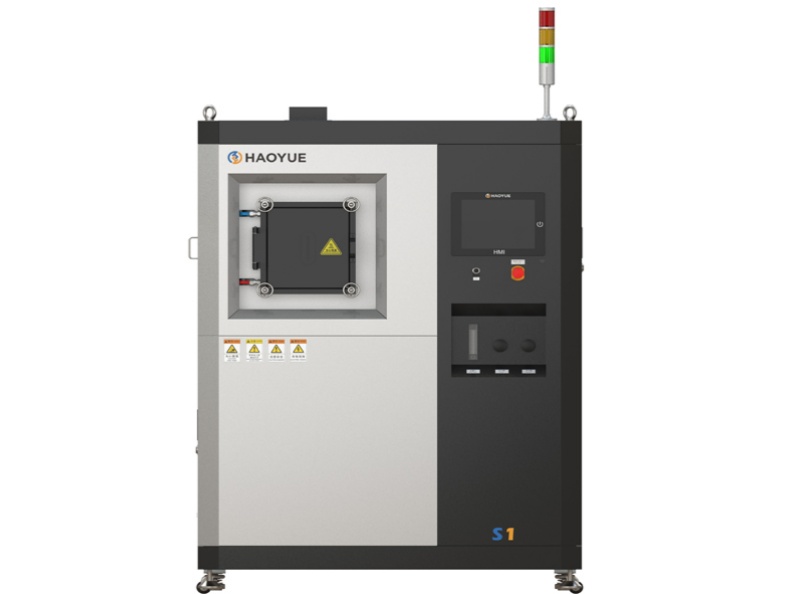
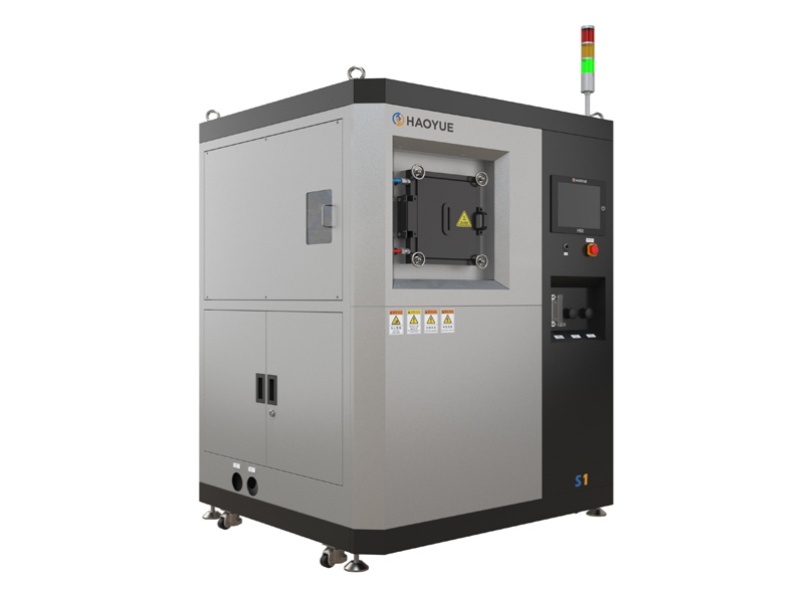
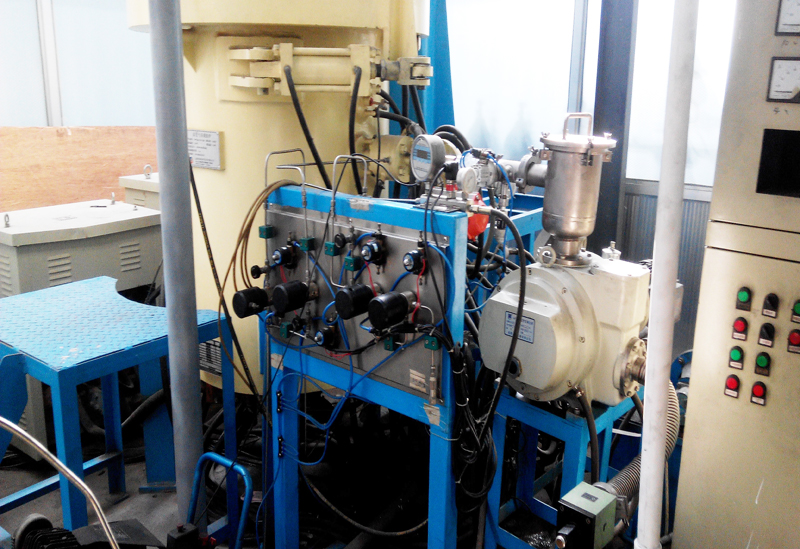
G3 Gas pressure Vertical Sintering Furnace
Gas pressure sintering furnaces are particularly useful for sintering ceramics or metals that tend to decompose at high temperatures or do not sinter to high densities in standard sintering operations. This process has no limitations of hot pressing in terms of making the shape of the part, and it is also an alternative to the expensive HIP process.
Technical Data
| G3 Vertical Gas Pressure Sintering Furnace | |
| Model | PVSgr-30/50-2000 |
| Equipment Form | Vertical |
| Loading method | Vertical upper loading |
| Working Size | Φ300 * 500 mm(Diameter*Height) |
| Max.Power | 170KW |
| Max.Temperature | 2000ºC |
| Working Temperature | 1900ºC |
| Temperature Accuracy | ±1ºC |
| Temperature uniformity | ±5ºC |
| Max.Working Pressure | 9.8MPa |
| Max. working pressure | 9.0MPa |
| Heating Element | Graphite |
| Max.Vacuum | 5 Pa(empty furnace, cold state, purified) |
| Pressure Rise Rate | ≤2.0Pa/h(Empty furnace, cold state) |
| Thermocouple | W-Re5/26(C) |
| Cooling Method | Natural cooling or Forced gas cooling |
| Atmosphere | High Purity Nitrogen or Argon |
| Control Method | PLC+HMI |
Specifications
The gas pressure sintering furnace is mainly used by enterprises for hot isostatic pressing sintering of ceramics (such as silicon carbide, zirconia, alumina, silicon nitride, etc.) and metal materials (such as cemented carbide) under the condition of high pressure protective atmosphere. It is also suitable for pilot production in colleges, universities and scientific research institutions. It is suitable for sintering silicon nitride ceramic balls, ceramic tools and other materials in high pressure nitrogen or argon atmosphere. It is beneficial to increase the sintering density and improve the mechanical properties of the material.
Welcome to contact us for the high quality gas pressure sintering machine for sale!
Application
Gas pressure sintering furnace features
1. The gas pressure sintering equipment is designed and manufactured according to the requirements of class 3 pressure vessel standards, and 16MnR or 304 furnace shell is adopted.
2. The door lock of the furnace is a bolt or tooth meshed quick release flange, which is easy to operate, safe and reliable.
3. The furnace cover is lifted and lowered by electro-hydraulic method, which is easy to operate and reduces labor intensity.
4. The insulation material in the furnace is carbon deposition composite hard felt, and the heating element is graphite imported from Germany.
5. The temperature measuring element adopts the ultra-high temperature protective tube developed by our company, which is matched with tungsten rhenium thermocouple, and the service life of thermocouple wire is up to half a year.
6. The control system is plc+ touch screen, with complete safety interlock protection and alarm functions.
7. The high-pressure valves and pipelines are all American "Swagelok" brand or equivalent imported products, which are safe and reliable.
Gas pressure sintering furnace applications
Oxide Ceramics
Transparent Ceramics
Silicon Nitride
Cemented Carbide
Main Ingredients
FAQ
What is gas pressure sintering?
Gas pressure sintering, also known as GPS technology, is dewaxing at low pressure, sintering at normal pressure, and after reaching a state where only closed pores exist in the material, sintering is performed at high pressure to further densify and eliminate remaining pores faster . Materials produced using GPS technology outperform non-porous materials produced by conventional sintering methods in general mechanical properties.
How does a gas pressure sintering furnace work?
The sintering process compacts the powder into a solid by applying heat or pressure. The material is heated to a temperature below the melting point in a sintering furnace, causing the powder particles to bind together to form a dense mass.
What is the difference between annealing and sintering?
In the field of glass and ceramics, annealing refers to the stress relief of glass by heating it below its glass transition temperature. Sintering refers to the coalescence of powders by softening under the influence of heat treatment.